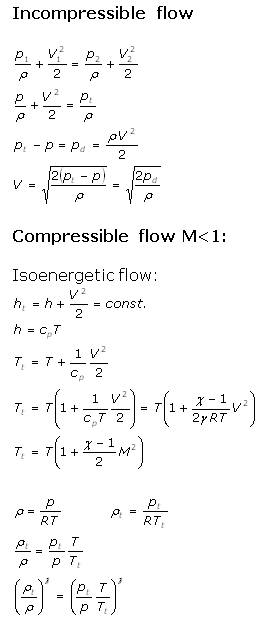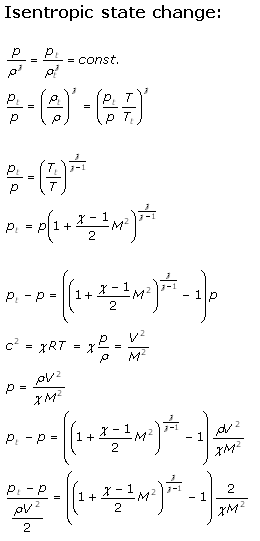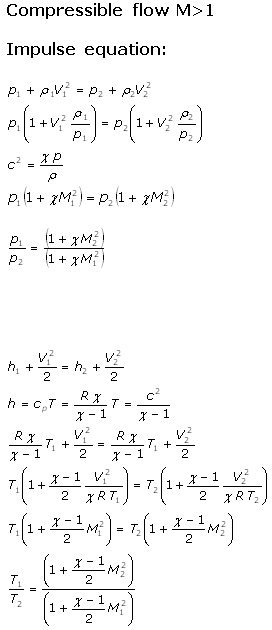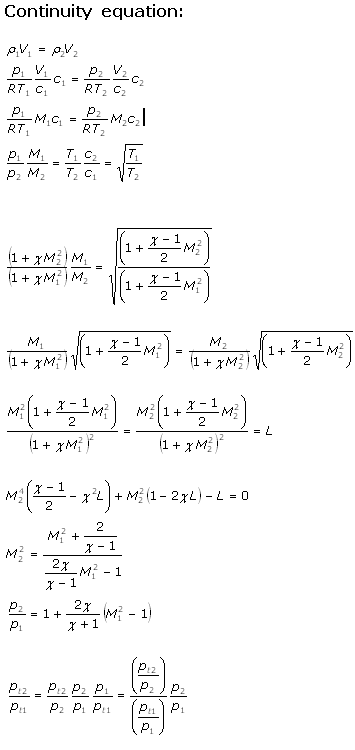Pitot Static Tube Online Calculation for Compressible and Incompressible Flow and Liquid
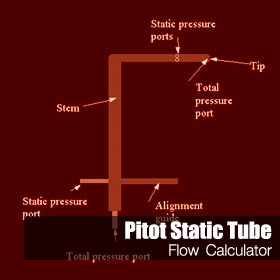 |
The Pitot Static Tube sometimes referred to as a Pitot Probe is a differential pressure device used as a flow meter for gases and liquids. It uses a differential pressure principle for the measurement using the known or measured static pressure and total pressure differences know as the dynamic pressure. Pressure can be measured using a manometer or pressure transmitter. This flow metering device is also known as the Prandtl Tube. Examples of other variations of the probe are the averaging pitot probe – see examples Notes on the use of this flow calculator are provided in this page. {loadposition java}
|
{source}
<applet archive=”PitotTube.jar” code=”com/flowmeterdirectory/start/PitotTubeStart.class” width=”550″ height=”500″>





 <param name=”mode” value=”online”>
<param name=”mode” value=”online”>





 <param name=”title” value=”Pitot tube Calculator”>
<param name=”title” value=”Pitot tube Calculator”>





 <param name=”copy1″ value=”Copyright Zoran Savovic 2000-2010. All rights reserved”>
<param name=”copy1″ value=”Copyright Zoran Savovic 2000-2010. All rights reserved”>





 <param name=”copy2″ value=”http://www.pipeflowcalculations.com”>
<param name=”copy2″ value=”http://www.pipeflowcalculations.com”>





 </applet>
</applet>
{/source}
Explanation of the Static Pitot Tube calculator values
pt – total pressure
p – static pressure
pd – dynamic pressure
rho – density
kappa – isentropic coefficient
R – gas constant
t – temperatire
D – diameter
V- velocity
M- Mach number
c- sound speed
Q – volumetric flow rate
G – mass flow rate
The Pitot Static Tube Calculation can be used to calculate for
V- velocity
M- Mach Number
c- sound speed
Q – volumetric flow rate
To calculate these values the inputs need are as follows
FOR LIQUIDS – Either pt and p – total pressure and static pressure or pd – dynamic pressure rho- density. D – diameter is optional only if Q and G need to be calculated
FOR GASES – p- static pressure either pt – total pressure or pd- dynamic pressure kappa – isentropic coefficient R – gas constant Either T – temperature or rho –density D- diameter is optional and needed only if Q and G need to be calculated
Equations used in the Pitot Static Calculator